Publication date: April 4, 2024
March 2024 Monthly Newsletter
Welcome to the March edition of our newsletter on the latest happenings in Japan’s power market. As cherry blossoms bloom across the country, signaling the early arrival of spring, we’re here to bring you fresh updates and insights into Japan’s dynamic energy landscape.
In this issue, we delve into key developments shaping the industry, including the latest FY2024 curtailment rate forecasts, the continuing downward trend of Feed-in Premium (FIP) prices for solar power, and an update on the status of carbon trading in Japan, six months post-launch. Join us as we navigate through the intricacies of Japan’s power market and uncover the trends shaping its future.
Forecasts Show FY2024 Curtailment Rates to Elevate in Most Areas

The Power System Working Group of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s (METI) Advisory Committee for Natural Resources and Energy has published its FY2024 curtailment forecasts for renewable energy (RE) sources. Curtailment is a nationwide occurrence in Japan due to various factors, including imbalances between supply and demand, Japan’s heavy reliance on imported energy fuels, increasing RE generation, and regional connectivity issues to the power grid. In an effort to reduce curtailment and promote the growth of RE, METI aims to compile its Curtailment Reduction Measures Package by the end of this fiscal year.
The Forecasted Curtailment Rates (The Numbers in Parentheses Are the FY2023 Forecasts)
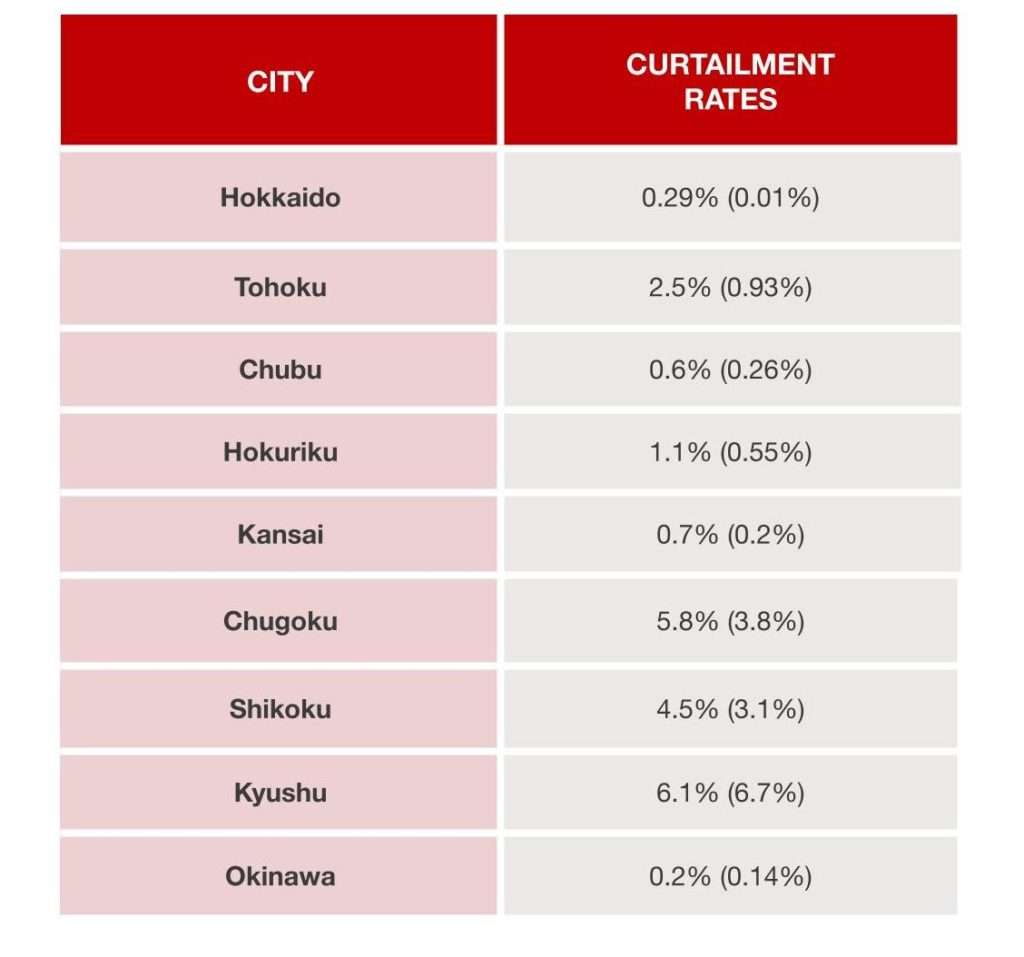
The most notable increase was in the Chugoku region, with a 2.0% rise attributed to more supply from the resumed operations of a nuclear power plant and decreased demand from the suspension of a pumped storage plant due to repairs. We anticipate a decrease in the curtailment rate in the Kyushu region, although it will likely remain in the 6% range due to the expectation of fewer sunny days.
FIP Solar Power Prices Continue to Decline

The Japanese government allocated 134 MW of capacity in its 19th tender for solar photovoltaic (PV) projects above 250kW, according to a report issued by the Organization for Cross-regional Coordination of Transmission Operators (OCCTO) on March 8th.
This auction established a ceiling price of JPY9.28/kWh, marking a JPY0.07 decrease from the previous rate of JPY9.35/kWh. They allocated a total of 134MW without distinguishing between Feed-in-Premium (FIP) and Feed-in-Tariff (FIT) projects. A total of 29 bids were successful, with demand surpassing supply by a factor of 2.32, an increase from 1.68 times in the previous auction. All successful bids came from projects over 500kW and contracted under FIP, which has been the recent trend. A significant development was the drop in the weighted average bid price from JPY8.55 in the previous auction to JPY5.11, largely due to an extra-high voltage project bidding at JPY0. Excluding this outlier, the weighted average would have been in the JPY6 range.
It is assumed that this JPY0 bid is a project selling electricity through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), thus not requiring FIP compensation but seeking government approval for the project plan. This trend in the tenders for PV projects reflects the evolving landscape of FIP and FIT auctions in Japan.
Carbon Trading Activity Reaches 200,000 Tons in Six Months

METI’s Working Group on Carbon Credits discussed the recent trends in the current carbon trading market, which was established in October 2023. They reported approximately 200,000 tons, totaling around JPY530million traded in the first six months, a significant increase from the demonstration phase in FY2023, which saw trading of approximately 150,000 tons, totaling JPY330million in the whole year. This increase in trading activity for renewable energy credits can be attributed to the introduction of the market maker system, which increased liquidity. The number of market participants also increased from 183 in FY2022 to 265 in FY2023.
The Working Group also began discussions on increasing the types of credits offered in the market.
Currently, the government sells 60 to 70% of the one million tons of J-credits created each year. The group proposed including credits that meet certain quality standards, including those from Direct Air Capture and Carbon Storage (DACCS), ahead of the full operation of the emissions trading system (ETS) scheduled for FY2025.
________________________________________________________________________________________
Thank you for reading. If you’ve enjoyed this content, subscribe to our complimentary monthly newsletter delivered straight to your inbox every month and stay updated with our latest offerings. Sign up here today.
