Publication date: Sept 2, 2025 Japan Moves to Develop Hydrogen and Ammonia Supply Chains
Japan Moves to Develop Hydrogen and Ammonia Supply Chains
Hydrogen (H₂) and ammonia (NH₃) are energy sources expected to be utilized in a wide range of sectors in Japan, including power generation, transportation, and industry (such as steelmaking). Japan drafted the Basic Hydrogen Strategy in 2017, which was the world’s first hydrogen development policy, and then revised the document in 2023. As a global leader in hydrogen, Japan has technological advantages based on research and development investments for hydrogen-based power generation and the use of hydrogen as a heat source in factories.
In this month’s newsletter, we take a closer look at recent developments in hydrogen and its close partner, ammonia.
–
Hydrogen and Ammonia’s Positioning in the 7th Strategic Energy Plan
In line with the revised Basic Hydrogen Strategy, the 7th Strategic Energy Plan (7th Plan) positions hydrogen and ammonia as key zero-emission fuels for power generation and industrial use by 2040–2050. The plan includes ambitious supply targets for both (see table below), with ammonia demand expected mainly as a hydrogen carrier and, to a lesser extent, as a direct fuel. These targets reflect the combined volumes of domestic production and overseas imports.
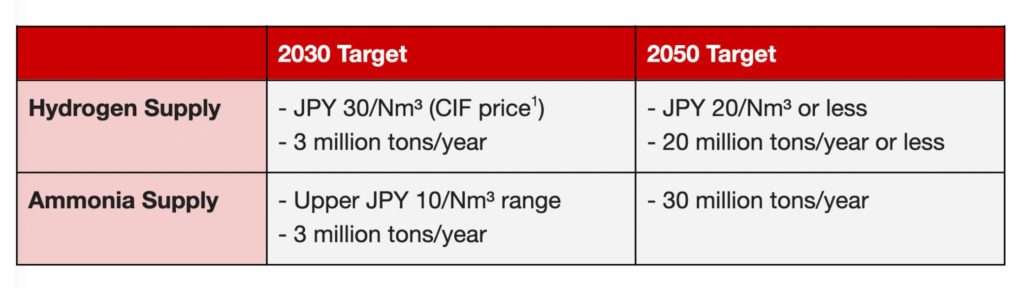
However, Japan’s hydrogen and ammonia roadmap is ambitious and hinges on several uncertain factors. Technological breakthroughs are still needed in production, transport, storage, and end use. For ammonia, METI targets 20% co-firing in coal plants by 2030, rising to 50% with dedicated combustion by 2050. Achieving this will require advances in efficiency, durability, and cost reduction. Strong institutional support is equally critical. The cost gap between fossil fuels and clean hydrogen remains wide, and demand-side uptake lacks sufficient incentives.
–
The GX Hydrogen Supply Chain Promotion Scheme
To narrow the cost gap with conventional fuels and support early-scale projects, METI launched the Hydrogen Cost Difference Compensation Scheme in 2024 under the Hydrogen Society Promotion Act, which provides the legal framework for such mechanisms. METI plans to allocate about JPY 3 trillion under this scheme to help first movers establish supply chains and scale up deployment, with the latest application round closed on March 31, 2025. METI will compensate for the price gap between the “Standard Price” set to allow cost recovery and the actual supply cost “Reference Price” for the first 15 years. For domestic supply, the scheme covers costs related to hydrogen and ammonia supply, and for imports, it also includes maritime transport to Japan.
Project proposals are assessed under two main criteria: 1) alignment with the government’s policies, such as GX policies, and 2) feasibility of the business plan for commencing by 2030 and continuing for 10 years after the 15-year support period.
*CIF price refers to the cost of goods including insurance and freight, delivered to the port of destination by the seller.
–
LTDA: Hydrogen and Ammonia Project Developments
The Long Term Decarbonization Auction (LTDA) provides long-term revenue support to accelerate investment in low-carbon power sources, including the introduction of hydrogen and ammonia power generation. Eligibility requirements include that bidders must be domestic corporations that directly operate and maintain power facilities. Bidders must submit detailed “decarbonization roadmaps” showing the pathway towards decarbonization by 2050, including staged increases in co-firing ratios and eventual transition to dedicated firing.
In the inaugural 2023 auction, 5.5 MW of hydrogen retrofits and 77 MW of ammonia retrofits cleared within the 1,000 MW procurement volume for this category. By contrast, the 2024 auction saw a decline in uptake, with only 9.5 MW awarded for ammonia retrofits from a single bidder, despite the procurement volume being unchanged.
In response, the eligible categories and price caps for hydrogen and ammonia projects are being revised for the FY 2025 auction (scheduled for October 2025) to ease entry conditions and encourage broader participation (see table below). However, the allocation size for hydrogen and ammonia-related projects will be halved from the previous auctions to a total of 500 MW.
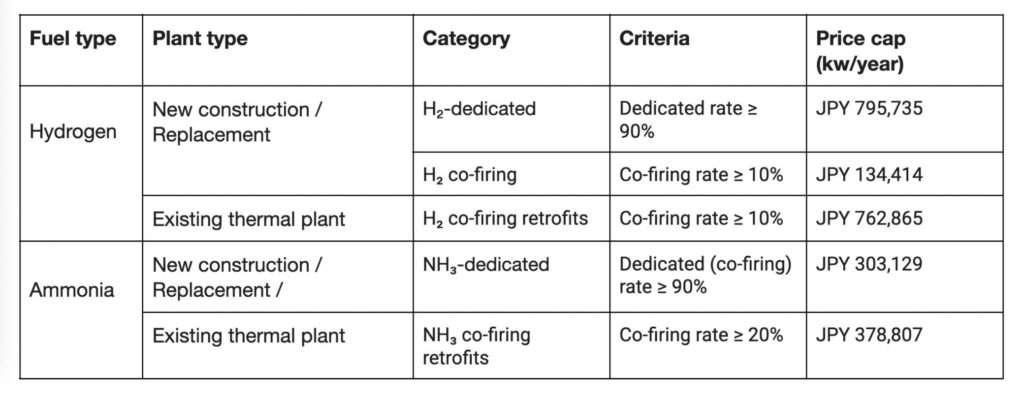
Source: OCCTO
Japan is expected to undergo significant changes as it transitions toward an economy that leverages the potential of hydrogen and ammonia, but realizing this shift still requires technological advances on both the supply and demand sides, as well as adequate government support. Our team closely monitors the evolving hydrogen and ammonia landscapes in Japan and can provide tailored analysis and strategic guidance to help navigate these developments and assess potential business opportunities.
Japan Moves to Develop Hydrogen and Ammonia Supply Chains
Thank you for reading.
If you’ve enjoyed this content, subscribe to our complimentary monthly newsletter. Get updates delivered straight to your inbox every month and stay informed about our latest offerings.
Sign up here today.
